Beware Malicious EIP-7702 Delegations: How to Protect Your Wallet from Instant Drains

Source: Malicious EIP-7702 Delegations and How to Stay Safe - support.relay.link
What Is EIP-7702 Delegation?
EIP-7702 is an Ethereum standard enabling wallets to delegate transaction authority to another contract. This unlocks advanced functions like account abstraction and smart wallets. However, if the delegated contract is malicious, it can control your funds the moment they land in your wallet.
How Do Malicious Delegations Work?
Attackers lure victims into signing dangerous delegations, often via fake free mints or giveaway sites. Once signed:
- The malicious contract can auto-drain tokens instantly when funds arrive.
- Some use fallback functions that immediately forward incoming balances.
- No extra transaction is needed-the theft happens within the same block the funds arrive.
Attack Flow Example:
- User signs a bad delegation.
- Attacker’s contract drains available funds and remains active for future deposits.
- When funds arrive through a bridge like Relay, they vanish instantly as the delegated contract forwards them out.
On-chain inspection shows the legitimate recipient wallet has no ETH balance because of this delegation:
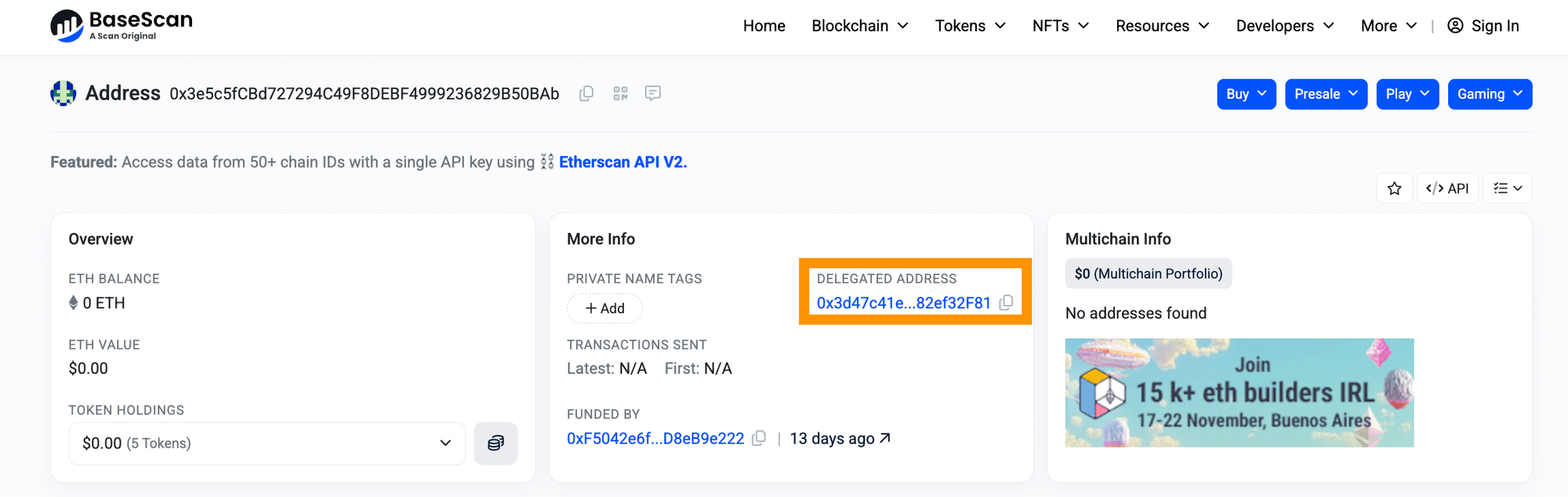
The wallet’s page confirms a Delegate Address has control:
Transaction details reveal funds hit the wallet, then are immediately forwarded to a third-party wallet set by the delegate:
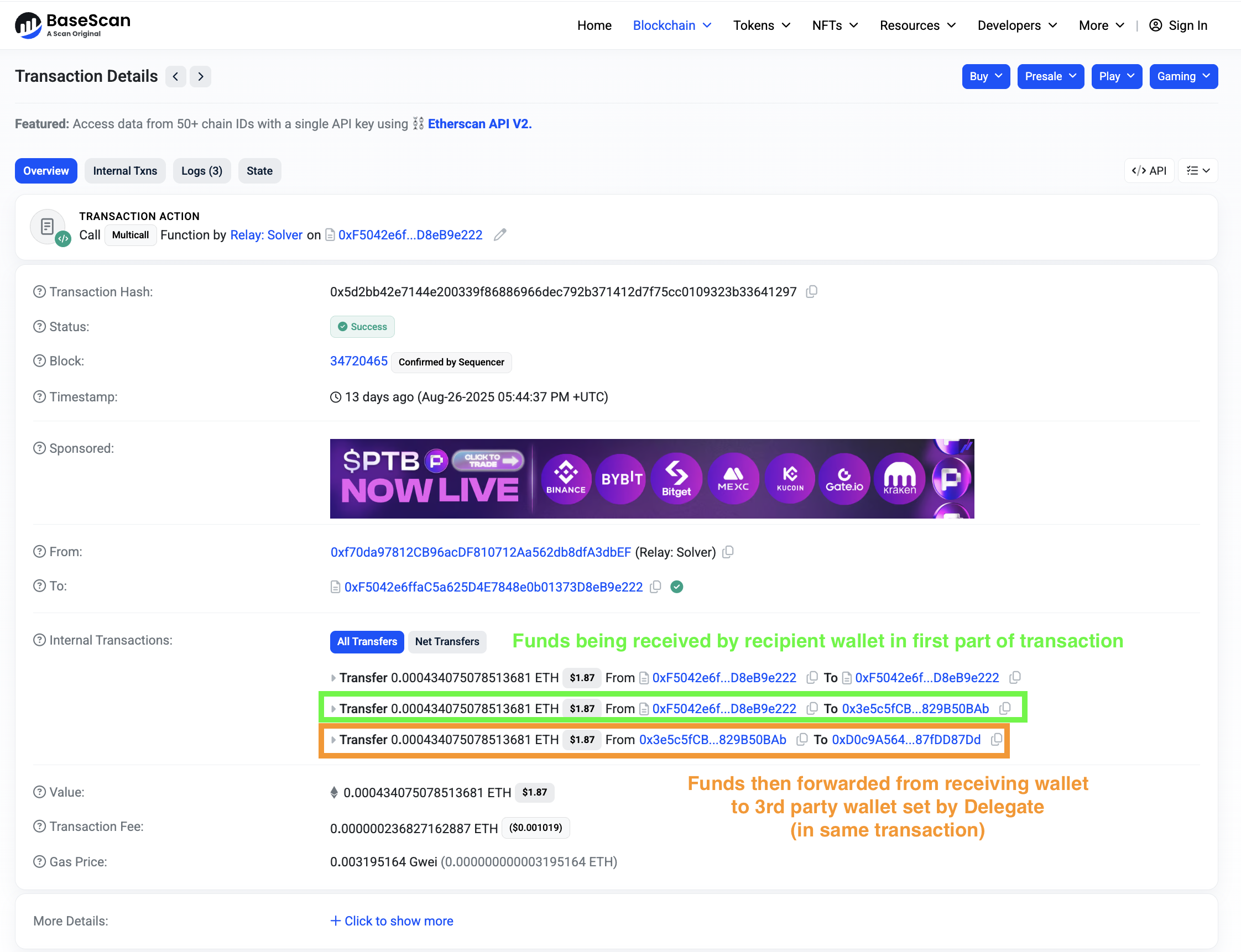
Important: The delegate address can differ from the final receiving address, which complicates spotting these scams.
Why Revoking Delegations Isn’t a Reliable Fix
- Most wallets don’t allow revoking delegations directly through their UI.
- Third-party revoking tools are emerging, but they may not fully eliminate risks.
- Unknown delegations usually mean your keys or seed phrase are compromised.
- Revoking creates a false sense of security.
- The safest action is to stop using the compromised wallet and transfer assets to a new one.
Misplaced Blame on Relay
Users often blame Relay for lost funds after swaps or bridges, but:
- Relay only delivers funds to your wallet correctly.
- The malicious delegation executes immediately after, making Relay look like the trigger.
- Attackers wait for big deposits, so Relay transactions become the visible drain point.
- Investigations always show the wallet was compromised before using Relay.
How to Protect Yourself
- Never sign delegation approvals from unknown or untrusted sources.
- Always read signature requests carefully.
- Treat any unknown delegation as a sign your wallet is compromised.
- Move assets promptly to a new, secure wallet.
- Use tools like Etherscan’s Wallet Delegation checker to monitor delegations.
What To Do If You Suspect a Malicious Delegation
- Stop using the wallet immediately.
- Transfer all recoverable assets to a new secure wallet.
- Don’t rely on revoking the delegation.
- Check other wallets you own for suspicious delegations.
- If the drain happened after a Relay transaction, contact Relay support with your wallet address and transaction hash.
Relay’s Response
Relay is actively working on:
- Detecting wallets with suspicious EIP-7702 delegations.
- Warning users before swaps or bridges into compromised wallets.
- Adding extra safeguards against these attack types.
Summary
EIP-7702 offers powerful wallet delegation but carries serious risks if abused. Unknown delegations likely mean wallet compromise – not just something you can revoke casually.
Stay vigilant: never approve delegations you don’t understand, and if compromised, switch wallets immediately. Relay is a delivery service, not the attacker, and is committed to user protection.


