TRON Smart Contract Security: Protecting Your Protocol Through Every Lifecycle Stage

Source: TRON Smart Contract Security Lifecycle | cantina.xyz
TRON stands out as a high-performance Layer 1 blockchain powering digital assets, stablecoins, and various content-focused protocols. It offers high throughput, fast finality, and minimal transaction fees, but these strengths bring unique security challenges that differ from Ethereum-based assumptions.
Understanding TRON’s Security Landscape
TRON’s underlying mechanics differ from Ethereum’s EVM in important ways, impacting:
- Execution behavior
- Resource (energy) consumption modeling
- Upgrade and governance patterns
Developers familiar with Ethereum defaults may unintentionally introduce vulnerabilities like state inconsistencies or overlooked attack surfaces when building on TRON.
A robust security lifecycle program involves comprehensive validation across architecture, implementation, operations, and incident resilience-aiming not just for correctness, but for clear system design under pressure.
Key Security Differences in TRON
Security audits must account for how TRON diverges from EVM norms, or they risk missing critical threats. These include:
- Different gas/energy consumption rules influencing transaction success
- Unique upgrade mechanisms impacting contract state
- Governance structures affecting control and revocation flows
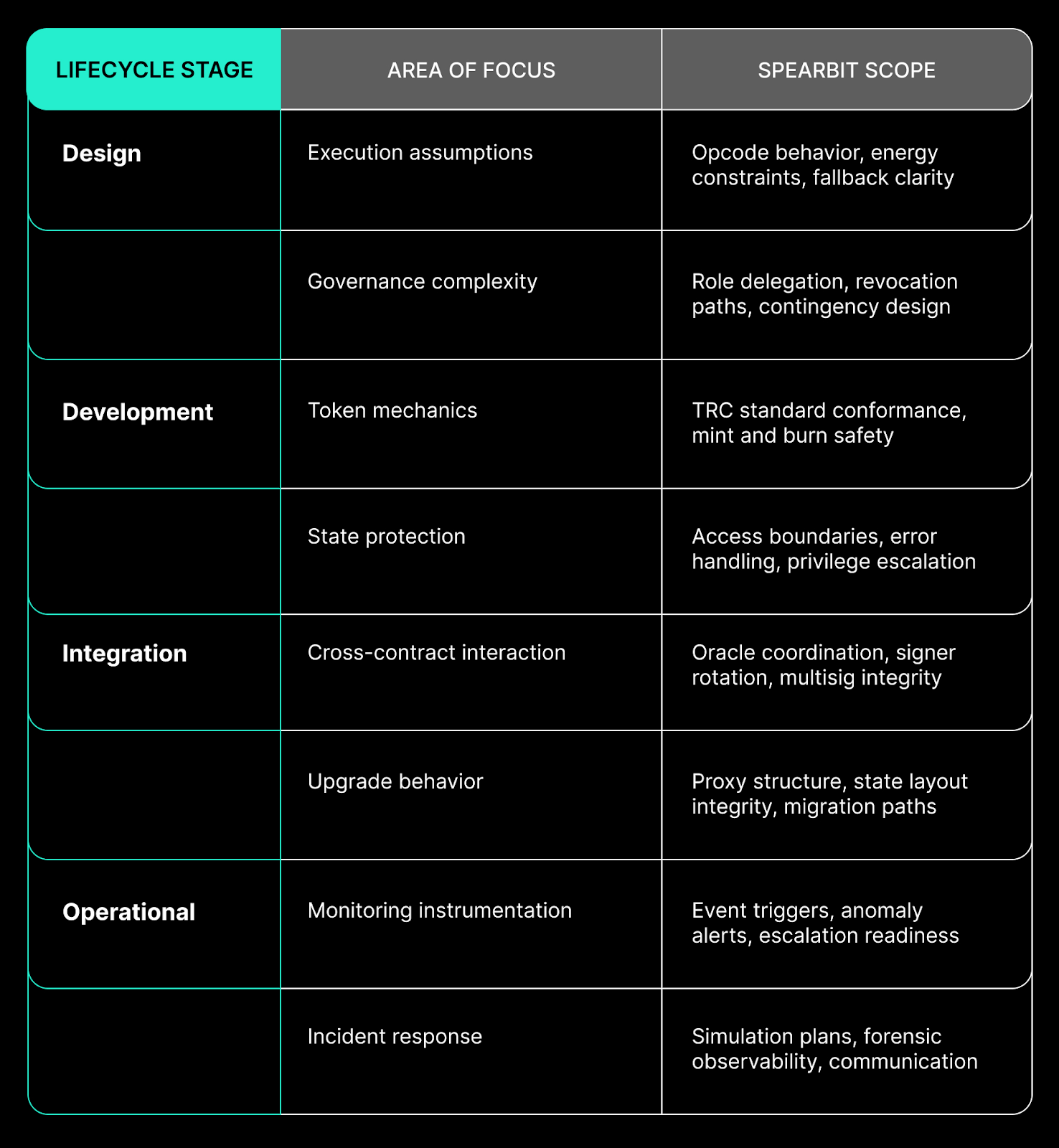
Securing Each Stage of the Protocol Lifecycle
Spearbit approaches TRON security with stage-specific validation:
- Design & Architecture: Formal analysis tailored to TRON’s unique features
- Implementation: Code reviews beyond usual modifier checks
- Operational Readiness: Access control, multisig, and roles management
- Incident Response: Monitoring, event hooks, and governance-aligned playbooks
Case Study: Oracle Failure from Energy Saturation
A recent audit exposed that under high market volatility, a decentralized exchange’s oracle drained nearly all available execution energy. This exhausted resource caused critical transactions-like liquidations and slippage adjustments-to silently fail without reverting, leaving users unaware of the issue.
Observed issues:
- Oracle logic worked during regular conditions
- Stress caused energy depletion preventing full transaction execution
- No user feedback on failed state changes
Remediations implemented:
- Profiling energy consumption on external calls
- Circuit breakers to curb resource overuse
- Redundant price feeds with tolerance for deviations
- Enhanced logging for detecting partial transaction outcomes
This problem only surfaced through lifecycle testing and simulations, highlighting the limits of static code review alone.
Operational & Governance Security
TRON’s governance relies heavily on delegated validators, which complicates access control. Overlooking revocation paths or role mismanagement can lead to major vulnerabilities.
Security assessments focus on:
- Multisig protections for upgrade authorities
- Clearly defined responsibilities across engineering and governance
- Secure key custody bound to validator duties
- Contingency plans for coordination failures
The goal: Implement security by design through transparent role and responsibility mapping, not reactive patches.
Post-Deployment Monitoring & Incident Preparedness
Strong monitoring extends beyond basic logs to high-fidelity signals correlated with actionable thresholds. TRON’s detailed event hooks enable structured observability such as:
- Custom mappings of privilege-changing events
- Transaction filters flagged for anomalous behavior
- Predefined triggers for coordinated containment measures
- Postmortem processes to reconstruct incidents accurately
Monitoring integrates directly with incident command systems, ensuring alerts translate into timely and effective responses.
How Spearbit Supports TRON Protocol Security
Spearbit’s tailored security services for TRON include:
- Design-phase validation focused on TRON’s distinct execution model
- Access control audits going beyond contract modifiers
- Simulations of upgrade processes and custody-related failures
- Comprehensive integration assessments across oracles, custodians, and pipelines
- Incident command playbooks aligned with the TRON governance framework
Effective TRON security requires synchronizing smart contract logic, infrastructure configuration, and governance structures into a resilient system.
Ready to protect your TRON project?
Begin a lifecycle security program with Spearbit to identify and address risks before production deployment tests your assumptions.


